Reference: Sep-Oct 2023 | Issue 5 | Vol 16 | Page 12
Start this Module
Module Title
Rheumatoid arthritis – The latest diagnosis and management approachesModule Author
Dr Aine Connerton and Prof Sinead HarneyCPD points
2Module Type
Case studyThe aim of this CPD module is to discuss the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), diagnosis and treatment. The complications of RA and how a multidisciplinary approach to care is needed for managing multisystem autoimmune diseases are also addressed.
Pathophysiology
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease of unknown aetiology. It affects approximately 1 per cent of European and North American adults, more commonly affecting women (3:1 ratio). The peak age of incidence is 50-to-60 years, but it can present at any age. Interestingly, in data published in 2019, Ireland has the highest incidence of RA at 38.6 per 100,000 population in Europe.1
What causes RA is unknown, however, there are several working theories. In RA, the innate immune system attacks synovium resulting in destruction of surrounding cartilage and bone. This erosive process leads to deformity, which results in loss of function, and can negatively impact the patient’s psychological mindset.
Two most common antibodies associated with RA are rheumatoid factor (RhF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA). Autoantibodies target the Fc part of the human IgG RhF in the blood of affected patients. RhF presents mostly as IgM RhF. RhF is also found in infectious diseases, other autoimmune diseases, and in up to 15 per cent of healthy individuals. ACPA-containing immune complexes can induce tumour necrosis factor (TNF) production by human macrophages. ACPA affects osteoclast activation, increasing the release of IL-8, which serves as an autocrine activator of osteoclast, which can result in the development of bone erosions.
Theories suggest this process is triggered in genetically-susceptible people by environmental triggers such as smoking, stress, infection, gut microbiome, and chance. The strongest genetic risk factor is in the HLA MHC Class II molecule encoding locus – HLA-DRB1 alleles. Genes for HLA-DRB1 on chromosome 6 are responsible for a number of immune processes, most notably modulation of TNF. This common amino acid sequence has been termed the shared epitope and individuals heterozygous for this have more aggressive and erosive disease, particularly if ACPA or RhF positive. Shared epitope homozygotes have higher risk of developing extra-articular manifestations of RA.2
Environmental factors such as tobacco smoking are associated with worse outcomes in patients diagnosed with ACPA-positive RA. Smoking increases the risk of RA onset in genetically-susceptible individuals 50-fold. Vaping and its effect on RA is yet to be explored.
Diagnosis
RA is diagnosed based on clinical, laboratory and radiological findings.
The 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) classification criteria3 were replaced by ACR/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) criteria in 2010.4 The classification criteria aid early detection of RA and help formulate diagnosis, which improves patient outcomes. However, they were designed originally for clinical trial use, to allow stratification of subjects into RA and non-RA cohorts. Seronegative patients need a larger number of joint involvement to fulfil criteria. If their condition doesn’t meet diagnostic criteria for definitive disease, patients are typically labelled undifferentiated arthritis. One-third of this cohort will develop RA, but 50 per cent will get spontaneous remission.3
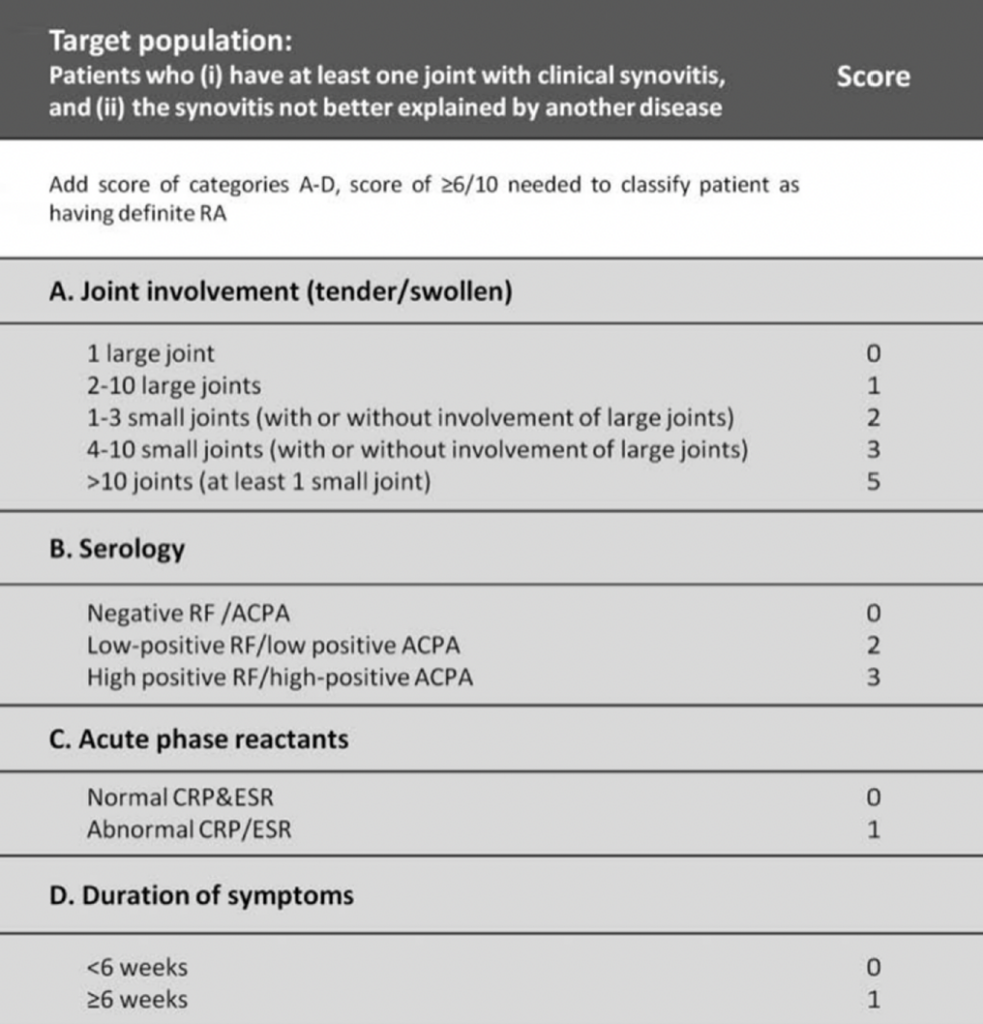
TABLE 1: ACR/EULAR criteria 20104
In the first consultation, detailed history taking and clinical examination remains pivotal.
Documentation of history should include:
–Symptoms of joint pain/swelling:
- Typically, RA presents with pain, stiffness and swelling in small- and medium-sized joints in symmetrical distribution. Less common is an acute presentation with fever, polyarthritis, and extra-articular manifestations or monoarthritis.
–Onset can be acute, insidious or palindromic.
–Discussing fertility, sexuality and family planning, particularly as RA has a predisposition for females:
- Teratogenicity of certain medications, as can determine the treatment plan.
–Family history of any underlying autoimmune disease particularly RA, uveitis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
–Recent infection:
- Reactive arthritis usually presents sub-acutely with asymmetrical monoarthritis or oligoarthritis, typically involving ankles and knees. Concurrent features may include urethritis and conjunctivitis.
Physical examination includes:
Assessment of all joints for synovitis using the ‘squeeze test’:
- Scoring systems such as the Disease Activity Score-28 (DAS-28) incorporates clinical findings and laboratory results. The most commonly involved joints in RA are metacarpophalangeal (MCP) 2 and 3, proximal inter-phalangeal (PIP) joints, wrist joints, and metatarsophalangeal (MTP).6
- Emery et al showed that the ‘squeeze test’ of MCPs and MTPs has rather low sensitivity (53 per cent and 54 per cent), and only moderate specificity (82 per cent and 74 per cent) for identifying arthritis. In saying that, it is a core component of our clinical examination.7
- Established RA cases may have Boutonnière’s deformity, Z-shaped thumb, (see Images 1 and 2) volar subluxation of MCP, dorsal subluxation of ulnar head, and clawing of toes.6
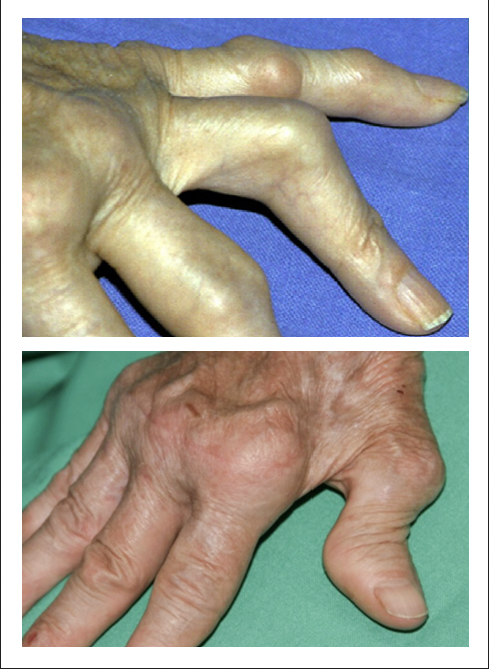
IMAGES 1 and 2: RA-related joint deformities
Extra-articular manifestations of RA should be looked for:
- Rheumatoid nodules;
- Splenomegaly when considering Felty syndrome;
- Serositis;
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Laboratory investigations
RA is a multisystemic disease and laboratory investigations are important for both diagnosis, drug monitoring, and management.
Initial work-up includes:
Full blood count looking for any abnormality, in particular thrombocytosis, leucocytosis, or anemia. Patients with RA can develop anaemia of chronic disease, drug-induced anaemia, iron deficiency, b12 deficiency anaemia, and myelodysplastic conditions.8
Renal function is checked, particularly given association with drug-related toxicities and IgA nephropathy.
Liver function tests are monitored regularly, especially when on treatment with csDMARDs, bDMARDs, and tsDMARDs.
Inflammatory markers such as CRP and ESR are used in validated scoring tools and classification criteria. Trending inflammatory markers throughout the disease course is beneficial for assessing response to therapy. Studies have shown monitoring serum ferritin as acute phase reactant as opposed to CRP and ESR is accurate.9 CRP and ESR are highly-sensitive markers but are lacking in specificity.
Antibody screening is important for prognostication of disease:
- RhF and ACPA. Other laboratory investigations that are commonly checked are immunoglobulins and extended antibody panels based off clinical context. Anti-SSA and Anti-SSB may be present given link with secondary Sjörgen’s.
Urine dipstick is useful, particularly for identifying early renal complications.
Biological screening. The tests included vary geographically so we recommend following local guidelines. In Ireland, a routine screen includes CXR, QuantiFERON or Mantoux test if no access to same, hepatitis screen, HIV test, VZV IgG, and baseline laboratory investigations.10
Radiology
X-ray, ultrasound (US), and MRI are the most common imaging modalities used.
There is more research supporting the use of US nowadays, given cost and easier access. X-ray of hands, wrists, and feet remain the ‘gold standard’ for diagnosing arthritis. Many patients have normal radiographs initially. Subtle changes such as periarticular osteopaenia and soft tissue swelling can develop in early arthritis.11 Erosions defined as typical for RA are cortical breaks on three separate joints at either PIP, MCP, radiocarpal or MTP joint regions.
Studies have shown presence of erosions on radiograph imaging of feet in the absence of symptoms. The prospective European multicentre ESPOIR trial showed that 10 per cent of patients had erosions detected on feet imaging without any at hand joints.12 The presence of juxta-articular bony proliferations on x-ray are typical for psoriatic arthritis. Modified Sharp van der Heijde is a validated scoring system used to assess the extent of radiographic damage. The risk of radiographic progression at five years is higher in the ACPA-positive population.13
US is a useful tool for the detection of subclinical synovitis, enthesitis, crystal deposition, and bone erosions. Grayscale and power doppler are established imaging techniques used. US can detect erosions of smaller joints earlier than conventional radiographs, particularly for MCP 2 and 5 and MTP 1 and 5. It is worthwhile examining wrists as extensor carpi ulnaris tenosynovitis can be an early presentation of RA.
This is advantageous as it promotes earlier intervention, allowing for ‘tight control’ of disease activity. A trial published in 2012 compared power doppler US measurements against OMERACT RAMRIS (RA MRI scoring system) scores for inflammation. Results were comparable, thus supporting the importance of US in clinical practice.14
MRI is more sensitive that other imaging modalities for the detection of rheumatic pathologies such as bone erosions, synovitis, osteitis, tenosynovitis, and cartilage destruction. CT lacks sensitivity for soft tissue pathology. The main limitation with MRI is the cost associated with it and lack of access. A study in 2015 highlighted the importance of MRI in seronegative patients to further classify undifferentiated arthritis.15 The presence of bone marrow oedema and synovitis on MRI can predict radiographic progression in RA.16
Treatment
Uncontrolled RA is associated with a six-to-seven year reduction in life. A holistic model of care is best practice and involves physiotherapy, occupational therapy, rheumatologist, specialist nurses, social work, and psychiatry.
Treatment decisions are shared between physicians and patients. It is important to identify patients expectations before commencing treatment, ensuring sufficient understanding of their disease. Treatment options have to factor in patient preference (tablet or injection), family planning, co-morbidities, and any safety issues. Education is a vital component of the consultation, particularly as patient’s may require multiple successive therapies throughout their life.
Historically, there were limited treatment options for RA. The first treatments focused on symptomatic relief in the form of anti-inflammatories and gold-based treatment. Over the past 25 years, our understanding of the pathogenesis of RA has switched our treatment focus to reducing inflammation through disease-modifying therapies (eg, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)).
Our treatment strategies remain guided by ACR/EULAR recommendations. EULAR’s latest update on RA treatment was published in 2022,17 with five overarching principles and 11 recommendations concerning use of conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs (methotrexate (MTX), leflunomide, sulfasalazine); glucocorticoids (GCs); biological (b) DMARDs (TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab including biosimilars), abatacept, rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs, namely the Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) tofacitinib, baricitinib, filgotinib, and upadacitinib.
Guidance on monotherapy, combination therapy, treatment strategies (treat-to-target) and tapering in sustained clinical remission is provided in EULAR’s latest guideline document. Safety aspects, including risk of major cardiovascular events (MACE) and malignancies, costs and sequencing of b/ tsDMARDs are also included.

FIGURE 1: EULAR 2022 update on RA management recommendations17
Initially, MTX plus GCs is recommended and on insufficient response to this therapy within three-to-six months, treatment should be based on stratification according to risk factors: With poor prognostic factors (presence of autoantibodies, high disease activity, early erosions or failure of two csDMARDs), any bDMARD should be added to the csDMARD; after careful consideration of risks of MACE, malignancies, and/or thromboembolic events tsDMARDs may also be considered in this phase.
If the first bDMARD (or tsDMARD) fails, any other bDMARD (from another or the same class) or tsDMARD (considering risks) is recommended.
With sustained remission, DMARDs may be tapered, but should not be stopped.
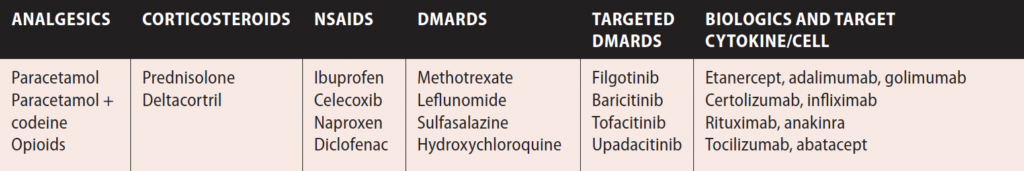
TABLE 2: Medications used in rheumatoid arthritis18
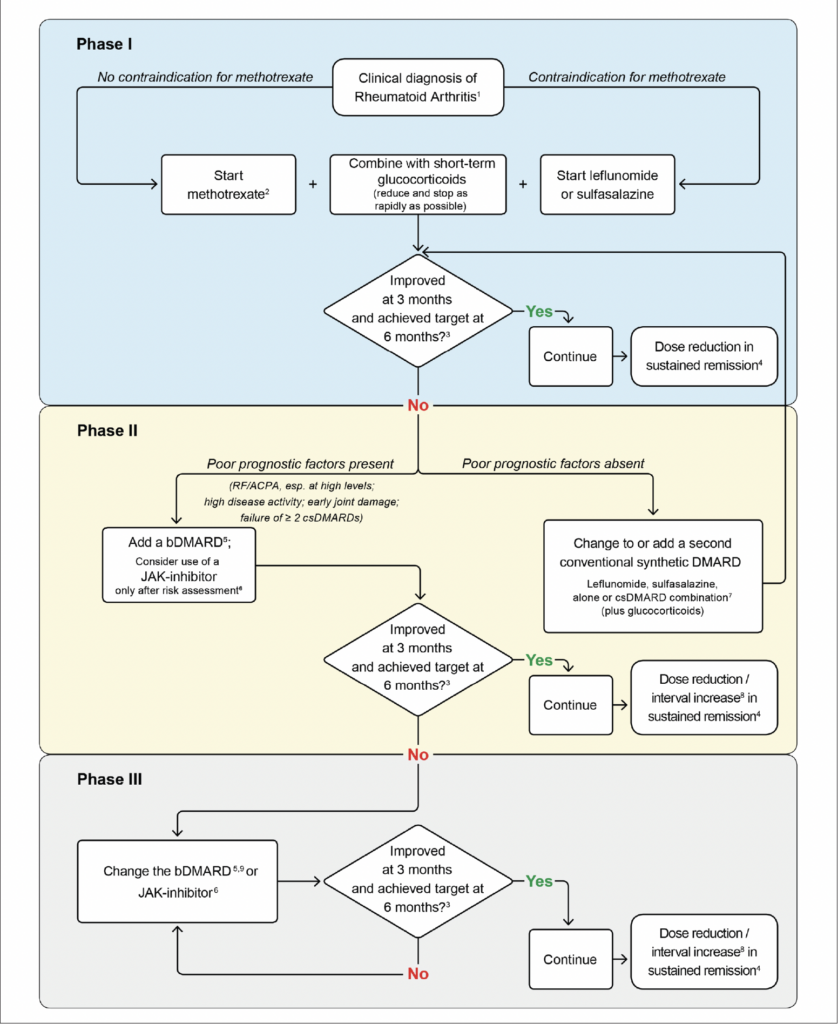
FIGURE 2: RA management flowchart (EULAR 2022)17
It is important to recognise poor prognostic indicators, which may mandate earlier intensification of therapy – such as antibody status, early erosions, failure of two csDMARDs and high disease activity.19
Scoring systems were developed for clinical trials to allow closer monitoring of disease activity such as DAS and ACR 20 (see Figure 3 below).20
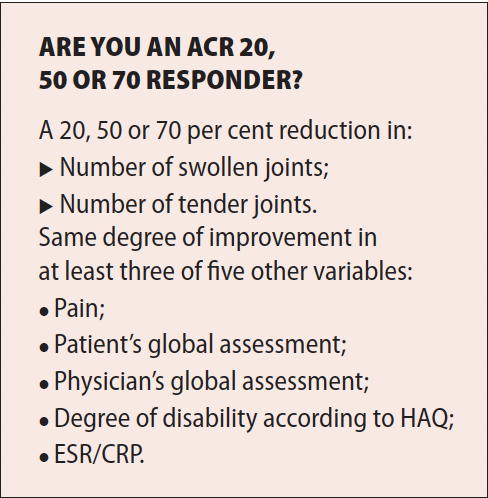
FIGURE 3: RA monitoring scoring system20,21
DAS-28 score (see Figure 4 below) is more commonly used.21 Cases in remission score <2.6 and severe cases score >5.1.
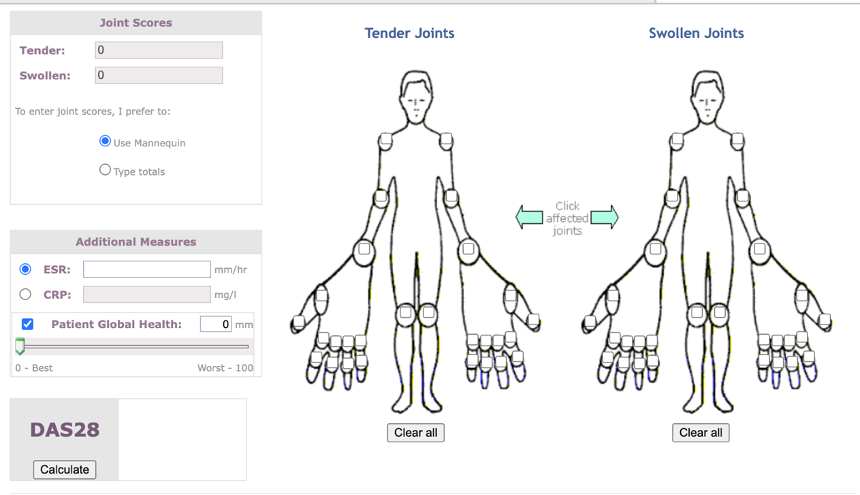
FIGURE 4: DAS-28 scoring system21
All patients with RA should be counselled on their general health – lifestyle measures and vaccinations are two core components of this. Live vaccines are contraindicated when on immunosuppressive therapy.
In difficult-to-treat RA, patients are at increased risk of developing complications or extra-articular manifestations such as:
Rheumatoid nodules22
- The most commonly found extra-articular manifestation, in up to 20 per cent of patients, usually at pressure locations.
- Mainly seen in seropositive patients.
Osteoporosis23
- Two-fold increase in development of same. It is likely due to the cumulative steroid dose throughout disease course, reduced mobility, and the inflammatory process increasing osteoclastic activity.
Cervical spine24
- Involvement of cervical spine is potentially life-threatening. It is diagnostic of atlantoaxial subluxation if the space between the anterior aspect of odontoid process and posterior surface of the arch of atlas exceeds ≥5mm. Radiographs with the head in neutral and flexed positions with lateral views are diagnostic.
- This can complicate surgical procedures requiring endotracheal intubation. However, the incidence of atlantoaxial subluxation is declining with initiation of early treatment.
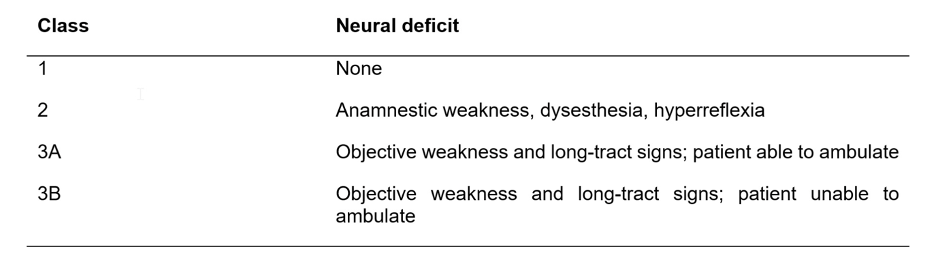
Cervical myelopathy25
- Occurs in ~2.5 per cent of RA patients.
- Tends to present with gait disturbance and loss of fine motor control in hands. Ranawat grading of cervical myopathy can aid diagnosis.26
- Treatment is directed by neurosurgery.
ILD27
- Can be caused by disease itself, infections, or drugs used. RA ILD is more common in males >60 years of age, smokers, and patients with higher disease activity. The most common subtype is usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia and organising pneumonia are less common, but the outcome is more favourable as they are highly steroid responsive.
- Treatments used are steroids, mycophenolate mofetil, rituximab, and more recently, anti-fibrotic agents.
Cardiovascular disease
- People with RA have a 50-to-70 per cent higher risk of developing coronary artery disease, than the general population.28
- Higher risk if seropositive.
- EULAR set out recommendations to mitigate this:
- Achieve disease control;
- Check individual’s risk using scoring systems such as Framingham;
- Screen for risk factors – obesity, smoking, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and cholesterol.29
Felty syndrome30
- <1 per cent of patients;
- Triad for diagnosis is splenomegaly, neutropaenia, and RA;
- Up to 30 per cent may develop large granular lymphocytic leukaemia (T-LGL). Risk increases with disease duration and antibody positivity.
Cancer
- Increased risk due to disease itself and drug therapies;
- Increased risk of lymphoma, particularly if long disease duration and antibody-positive disease;31
- Drug therapies such as anti-TNF agents are associated with increased risk of skin malignancy.32
Conclusion
The overall health of RA patients has improved over the last few decades, which is likely due to earlier diagnosis and more aggressive treatment strategies.












Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.